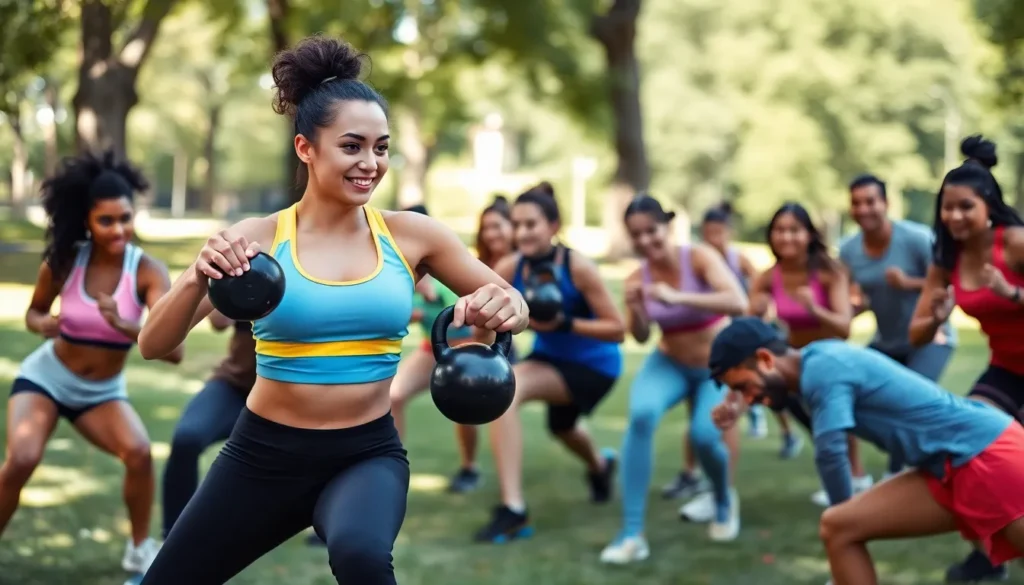Athletic performance is a fascinating blend of physical prowess, mental toughness, and strategic thinking. Whether on the track, field, or court, athletes push their bodies to the limit, striving for excellence in every competition. Understanding the factors that contribute to peak performance can unlock new levels of achievement for both amateur and professional athletes alike.
From nutrition and training regimens to psychological preparation and recovery techniques, the elements influencing athletic performance are vast and interconnected. As sports science continues to evolve, so does the ability to enhance performance through innovative methods and technologies. This exploration into athletic performance not only highlights the dedication required but also reveals how small adjustments can lead to significant improvements in an athlete’s journey.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Athletic Performance
Athletic performance encompasses a variety of elements that contribute to an athlete’s success in their chosen sport. Key factors such as physical conditioning, mental toughness, and tactical approaches play significant roles in achieving peak performance.
Factors Influencing Performance
- Physical Conditioning: Endurance, strength, flexibility, and speed are critical components that define an athlete’s physical ability. Every sport requires a unique combination of these elements to optimize performance.
- Nutrition: Proper nutrition fuels the body, enhances recovery, and supports overall health. Athletes must tailor their diets to include macronutrients and micronutrients that promote performance improvement.
- Mental Resilience: Mental toughness enables athletes to cope with stress, overcome challenges, and maintain focus. Positive self-talk and visualization techniques can enhance confidence and performance.
- Genetics: Genetic predispositions can affect an athlete’s physical traits, including muscle fiber composition and aerobic capacity, influencing their potential in specific sports.
- Recovery Techniques: Appropriate recovery strategies, such as sleep, hydration, and physiotherapy, allow athletes to mitigate fatigue and prevent injury, contributing to sustained performance.
Importance of Training
- Skill Development: Regular training hones the technical skills necessary for effective competition. Focused practice ensures athletes develop their abilities continuously.
- Performance Consistency: Structured training regimens build muscle memory, enabling athletes to execute skills consistently under pressure.
- Injury Prevention: Training that incorporates strength and conditioning reduces the risk of injuries. Proper techniques and conditioning improve resilience against performance-related injuries.
- Adaptation to Stress: Training exposes athletes to controlled physical stress, allowing them to adapt, strengthen their bodies, and improve their performance capacities.
- Monitoring Progress: Systematic training enables athletes to track improvements over time. Utilizing feedback helps identify areas for development and adjust training strategies accordingly.
Types of Athletic Performance

Athletic performance can be categorized into distinct types based on the demands of various sports. Key areas of focus include endurance, strength, speed, and agility, each contributing unique aspects to overall performance.
Endurance vs. Strength
Endurance reflects an athlete’s ability to sustain prolonged physical activity. It’s essential for sports like marathon running and cycling. Athletes train through long-distance runs, interval workouts, and cross-training to enhance aerobic capacity.
Strength focuses on an athlete’s ability to exert force against resistance. This type is crucial in sports such as weightlifting, football, and wrestling. Strength training includes weight lifting, resistance exercises, and plyometrics to develop muscle power and mass.
Speed and Agility
Speed measures how quickly an athlete can move from one point to another. It’s vital in sports requiring quick bursts of movement, such as sprinting, soccer, and basketball. Training methods like sprint drills, acceleration workouts, and agility ladders enhance speed.
Agility refers to an athlete’s ability to change direction rapidly while maintaining control. Sports like basketball and tennis rely heavily on agility. Drills such as cone drills, shuttle runs, and footwork exercises improve this skill.
Each type of athletic performance plays a crucial role in determining an athlete’s effectiveness and success in their chosen sport.
Measuring Athletic Performance
Measuring athletic performance involves various methods that provide insights into physical capabilities and overall effectiveness in sports. This process includes fitness assessments and performance analytics, both essential for enhancing training strategies.
Fitness Assessments
Fitness assessments evaluate an athlete’s physical condition through standardized tests. These assessments focus on key fitness components, including:
- Endurance: Tests such as the beep test measure cardiovascular fitness by assessing the body’s ability to sustain prolonged exercise.
- Strength: One-repetition maximum tests gauge the maximal strength of specific muscle groups, crucial for sports requiring power.
- Flexibility: Sit-and-reach tests measure the range of motion in key muscle groups, impacting movement efficiency and injury prevention.
- Speed: Sprint tests, such as the 40-yard dash, assess how quickly an athlete can cover a distance, relevant for sports emphasizing rapid acceleration.
These fitness assessments create a baseline for monitoring progress, tailoring training regimens, and identifying areas needing improvement.
Performance Analytics
Performance analytics utilizes technology and data analysis to assess an athlete’s capabilities and tactics during training and competition. Techniques in performance analytics include:
- Wearable Technology: Devices like heart rate monitors and GPS trackers collect real-time data on an athlete’s performance metrics, including speed, distance, and recovery time.
- Video Analysis: Reviewing game footage allows coaches and athletes to analyze techniques and strategies, identifying strengths and weaknesses in performance.
- Biomechanical Analysis: This examines the body’s movements through high-speed cameras and force plates, providing precise data on technique efficiency and potential areas for injury risk.
By integrating performance analytics, athletes optimize training strategies and enhance performance outcomes based on objective data.
Nutrition and Athletic Performance
Nutrition significantly impacts athletic performance by providing the necessary fuel and nutrients for optimal functioning. An athlete’s diet must cater to their specific needs, enhancing performance and recovery.
Role of Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in sustaining energy levels, supporting recovery, and enhancing overall performance. Macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—serve different purposes:
- Carbohydrates: Carbs are the primary energy source. They replenish glycogen stores, crucial for endurance and high-intensity activities.
- Proteins: Proteins aid in muscle repair and growth. Consuming adequate protein post-workout maximizes recovery and muscle synthesis.
- Fats: Healthy fats provide long-lasting energy, especially during prolonged or low-intensity activities.
Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins ensures a well-rounded intake of vitamins and minerals, supporting long-term health and performance.
Supplements and Hydration
Supplements can enhance performance when dietary intake falls short. Common supplements include:
- Protein powders: Aid in meeting daily protein needs, especially for athletes undergoing intense training.
- Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs): Help reduce muscle soreness and fatigue during workouts.
- Creatine: Supports strength and power output by increasing phosphocreatine stores in muscles.
Hydration remains a vital aspect of nutrition. Maintaining proper fluid balance helps prevent dehydration, which can impair performance. Athletes should consume water before, during, and after physical activity. Depending on intensity and duration, electrolyte drinks can replenish lost minerals and maintain optimal hydration levels.
Focusing on nutrition and hydration not only enhances athletic performance but also contributes to long-term health and well-being.
Psychological Aspects of Athletic Performance
Psychological factors significantly impact athletic performance, influencing an athlete’s ability to focus, cope with pressure, and maintain motivation. Understanding these aspects is essential for optimizing performance in competitive environments.
Mental Training Techniques
Mental training techniques enhance focus, confidence, and resilience in athletes. Visualization involves imagining successful performances, which can improve execution during competitions. Positive self-talk encourages athletes to maintain a constructive mindset, boosting confidence and reducing self-doubt. Goal setting provides clear targets, leading to enhanced motivation and a sense of accomplishment as athletes achieve incremental milestones. Mindfulness practices help athletes concentrate on the present moment, reducing distractions during training and competitions. Incorporating these techniques regularly into training regimens fosters mental toughness, essential for high-stakes performance.
Overcoming Performance Anxiety
Performance anxiety can hinder athletic performance, often manifesting as nervousness or fear of failure. Identifying triggers, such as high-pressure situations or intense competition, allows athletes to prepare strategically. Breathing exercises promote relaxation and calmness, serving as effective tools to manage anxiety. Developing pre-performance routines can create a sense of familiarity, helping athletes enter a focused state. Seeking support from coaches or sports psychologists can provide valuable coping strategies and foster resilience against anxiety, ensuring athletes perform at their best even under pressure.
Athletic performance is a complex interplay of various factors that go beyond mere physical ability. It requires a holistic approach that incorporates nutrition, mental resilience, and strategic training. By understanding the specific demands of their sport and tailoring their training accordingly, athletes can unlock their full potential.
Emphasizing recovery and psychological preparation is crucial for maintaining peak performance. As sports science continues to evolve, athletes have access to innovative tools and techniques that can significantly enhance their capabilities.
Ultimately, the commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation is what sets successful athletes apart in their pursuit of excellence.